PNG vs JPG: Which is better for your website?
PNG vs JPG : Which is better for your website? Visual appeal is crucial in web design. It has the power to attract, trigger emotions, and ultimately improve your site’s traffic. There are a number of components that contribute to the overall beauty of a website.
Images are one of them. But beyond making your site beautiful, images tell stories and give life to your text. They convey information and make them easy to comprehend.
Yes, images are great! But the image file format matters too. Using the right format for the right purpose means your design would appear just as you planned. And you will get the best balance of image quality and size.
Although there are dozens of image formats available, JPG and PNG are two of the most commonly used image formats on the internet.
Let’s take a quick look at the features of JPG and PNG and the differences between both file formats.
Content:
- Why should you care about image formats?
- About JPEG
- About PNG
- JPG vs PNG: Compression
- PNG vs JPG: Size
- JPG vs PNG: Transparency
- Compressing an Image
- Conclusion.
Why should you care about image file formats?
As stated earlier, there are dozens of image file formats available. Why should you bother about them?
Well, as simple as it may seem, a wrong format could mean a bad web image, a missing detail, or a large download. Let’s see this in greater detail.
Site’s loading time:
This subject is very dear to every website owner. Multiple studies show that if a site’s loading speed exceeds 3 seconds, the abandonment rate increases.
Heavy images mean longer loading time. On the contrary, lighter images result in faster loading time and could improve your site’s performance.
Now, some image formats are heavier than others. It would make a lot of sense to utilize lighter images on your site.
Site’s appearance:
Anyone can tell when an image lacks good quality. Blurred and low-quality images could send a wrong message about you and your brand.
Some file formats provide better-looking images than others.
Whichever format you use, there should be a balance between quality and performance. Let’s have a look at both file formats (PNG and JPG) and their features.
About JPEG
JPEG stands for Joint Photographic Experts Group and was developed in 1992. It is a lossy compressed image format. This means the image quality reduces as you compress it.
This is an ideal format for the web and is a great choice for saving photographs and images with complex colors and shadings. Just like the image below:
JPEG files are one of the most popular file formats on the internet for obvious reasons. They are small in size, are easy to load, and can contain over 16 million different colors.
If you need to share a photograph, JPEG is your best option. It is adequately optimized for photography and is supported across a wide range of platforms.
Side note: JPG and JPEG are the same. The original extension for the Joint Photographic Expert Group image format was ‘JPEG’. But, Windows (earlier versions) required a three-letter file extension, hence reducing JPEG to JPG. However, Linux uses JPEG since it had no such requirement.
About PNG
PNG (pronounced as ‘ping’) stands for Portable Network Graphics and was first released in 1996. It was developed as a non-patented and enhanced version of the Graphics Interchange Format (GIF).
This type of image format is best used for storing files with fewer colors like graphic works, illustrations, and screenshots. It is a lossless compression file format. This means it retains an image’s quality even after reducing its file size.
PNG images are usually large files and are not so good for photographs. They are better used for images with some text or line art. This is because PNG does a great job of making the contours of the letters and the fine lines from graphics appear sharp.
PNG file type also gives you control over transparency which makes it a good choice for saving logos.
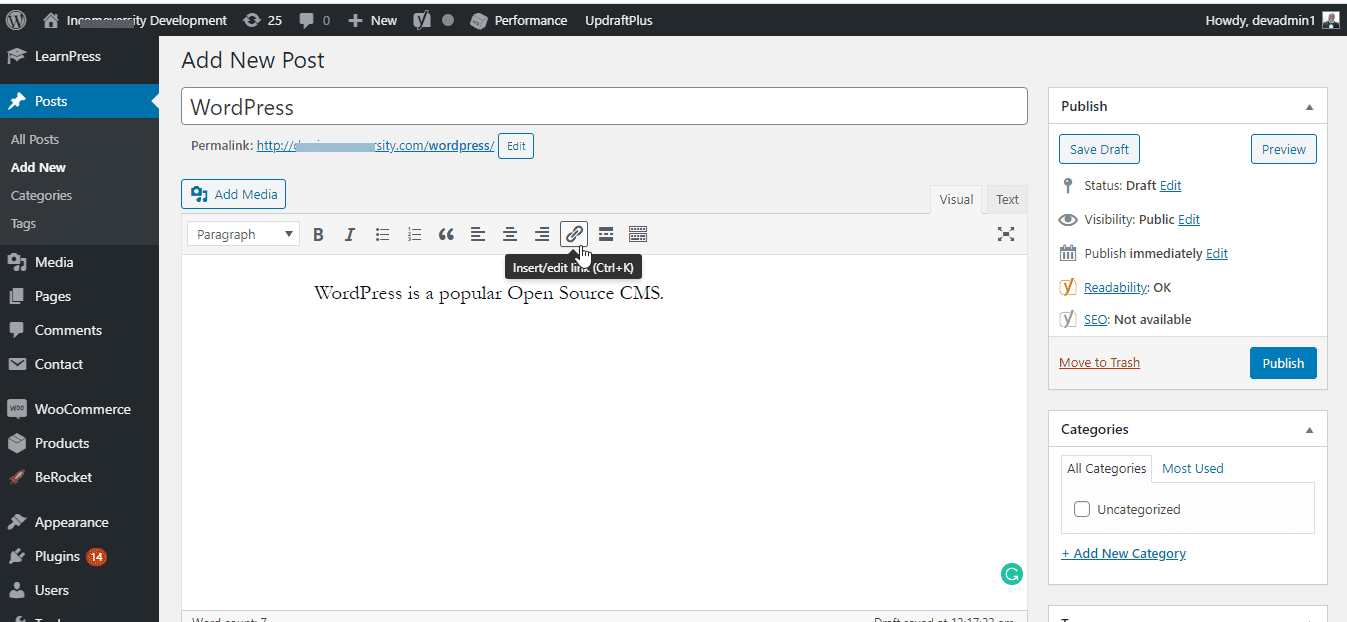
The screenshot below was saved in PNG format.
You can clearly see the letters, the dark and light backgrounds, and the sharp lines.
PNG vs JPG: Compression
JPEG and PNG use different compression methods or codecs to store a file’s data.
To start with, JPEG relies on DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform) compression. This technique works by dividing an image into parts of differing frequencies. Then, it eliminates the less important frequencies. This is why we say JPEG is ‘lossy’.
While this method is efficient, certain ‘unnecessary data’ are permanently lost. As a result, each time you open, make changes and save a JPEG file, there would be a quality drop. Although, this drop in quality may go unnoticed.
PNG, on the other hand, relies on LZW (Lempel-Ziv-Welch) compression. It is a lossless data compression algorithm that results in the same quality image. PNG provides a near-perfect representation of an image. This is its biggest disadvantage over JPEG images.
PNG vs JPG: Size
Real-life photos and images with many colors are smaller in size when you save them in JPEG format.
Here is a side-by-side image of a flower in both formats.
Obviously, JPEG is a fine choice for photographs and real-life images because you end up with much smaller files. Saving the image in PNG format would consume more space and bandwidth.
PNG file sizes, on the other hand, are smaller for illustrations, logos, line art, etc.
The above screenshot was saved in PNG format and has a file size of 67.5KB. In JPEG format, it is 3.5KB heavier, weighing in at 71KB.
In summary, saving real-life, color-filled photos, and graphics in JPEG format results in smaller files and better images. On the other hand, screenshots, logos, and the likes are better saved in PNG format for smaller file sizes and better quality.
PNG vs JPG: Transparency
PNG supports transparency while JPEG doesn’t. This lets you create images that overlay flawlessly with your site’s content. Like this:
Most editing programs use a checkered background to show the transparency of an image. This feature is great for logos.
JPG, on the other hand, has a non-transparent background.
Compressing your Images
Regardless of the file format you use (JPEG or PNG), you may need to optimize/compress your images for the web. This would mean a smaller sized image, more memory space, and a fast website.
How do you compress images for the web? There are two ways.
The first method involves the use of image editing software (like Photoshop) before uploading the image to your website. This process gives you more control over your image quality.
If you aren’t comfortable using an image editing software, there are WordPress plugins for you.
The plugins optimize your image files by compressing them automatically while retaining their quality as much as possible.
Let’s see some of the tools used for optimizing your images.
WP Smush
This WordPress plugin lets you optimize your images, and resize and compress them without a visible quality drop. With over 1 million active installs and an almost perfect 5-star rating, it sure is a crowd-favorite plugin.
Compress JPEG and PNG images
This plugin compresses and optimizes JPGs and PNGs by integrating with TinyJPG and TinyPNG image compression services. On average, PNG images are automatically compressed by 50-80% and JPG images are compressed by 40-60% without obvious loss in quality.
The Kraken WordPress plugin
This plugin lets you compress and optimize your images (JPG, PNG, and GIF formats) through Kraken.io Image Optimizer’s API. It supports both lossy and lossless optimization modes.
PNG vs JPEG – Conclusion
So, PNG vs JPEG: which is better for your site? As you must know by now, the answer is “it depends”.
They both serve different purposes well.
JPG formats are best suited for real-life images, and images with many colors like photographs. PNG is ideal for line drawings, charts, iconic graphics, illustrations, document scans, architectural plans, logos, or any image with text.